What are carbon credits?
Carbon credits, or carbon offsets, refer to carbon emissions reductions or removals, measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e).
Carbon credits can be generated through projects which take in carbon (e.g. reforestation), or reduce the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere (e.g. renewable energy projects).
There are four general stages of a carbon credit’s lifecycle.

Carbon credits support climate action by unlocking much-needed capital for mitigation projects which otherwise would not be implemented.
Carbon markets accelerate climate action by unlocking capital for emission reduction or removal projects globally, which would otherwise not be implemented. Carbon credits can also advance sustainable development and provide co-benefits to local communities.
Examples of carbon projects and co-benefits.

Under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, countries can trade Internationally Transferred Mitigation Outcomes (ITMOs) to achieve their climate targets
Article 6 of the Paris Agreement sets out the framework for countries to voluntarily cooperate to achieve their climate targets, otherwise known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
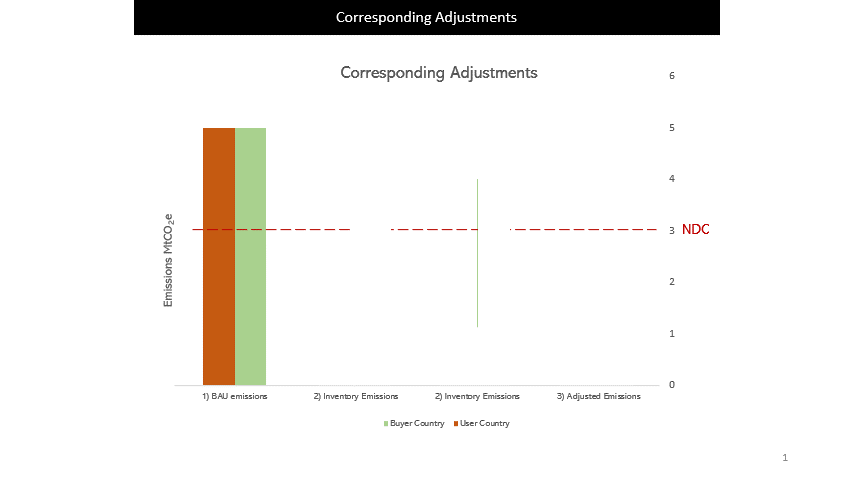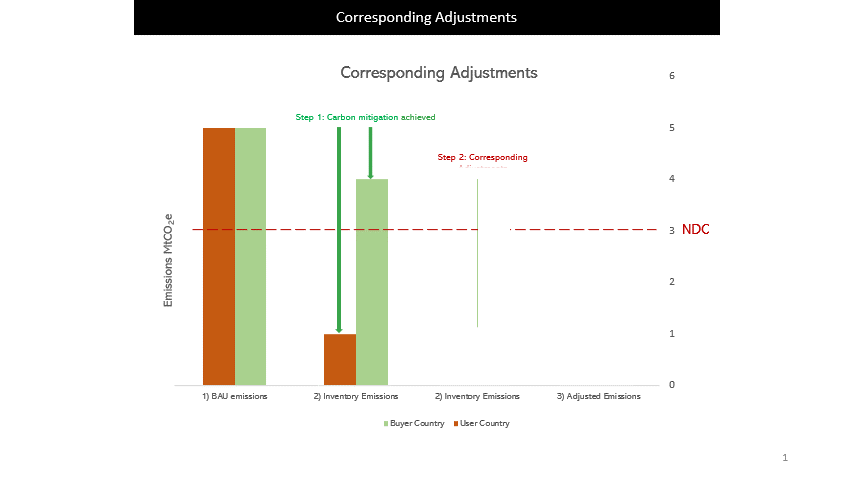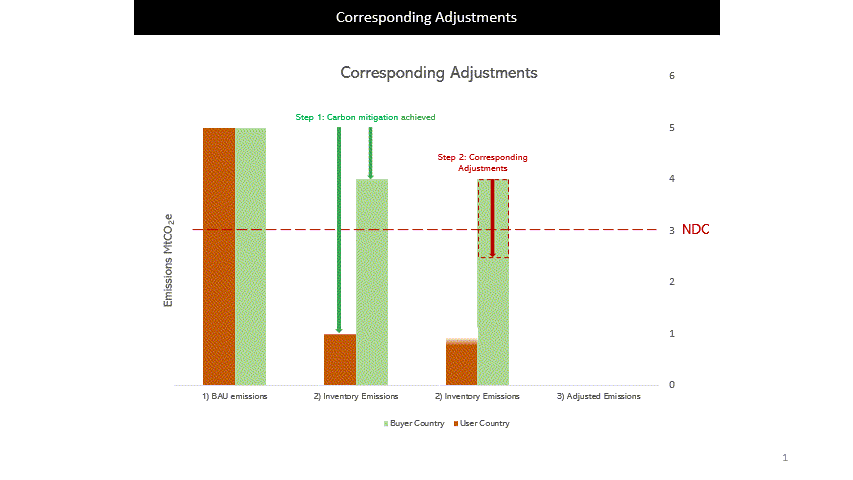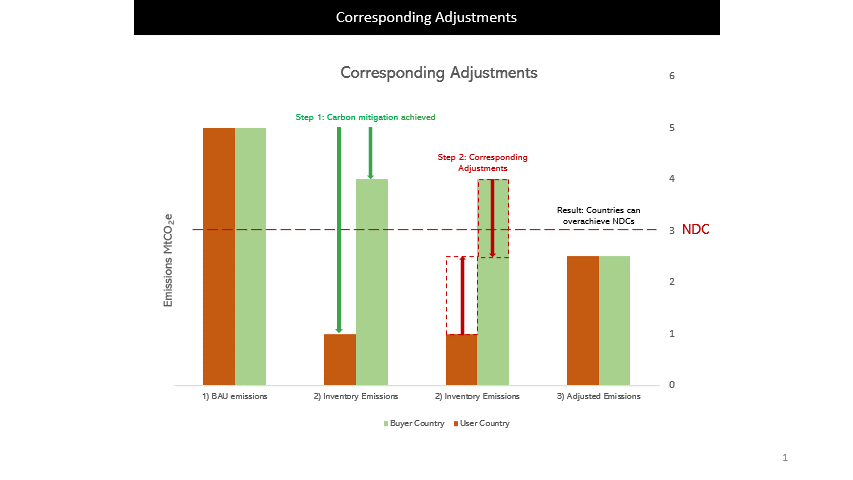
Through enabling the trading of Internationally Transferred Mitigation Outcomes (ITMOs), host countries could potentially go above and beyond their unconditional NDCs, which are commitments that host countries intend to achieve without external support.
For ITMOs to be used towards the buyer country’s NDC, the host country would need to apply Corresponding Adjustments (CAs) to ensure no double counting of emission reductions and removals.
For example, when Country X buys 1MtCO2e of carbon credits from Country Y, Country Y has to add 1MtCO2e to its GHG inventory while Country X will reduce 1MtCO2e in its GHG inventory.